DeepSeek Coder- Developer Guide

DeepSeek Coder is a cutting-edge series of code language models trained from scratch on 87% code and 13% natural language in English and Chinese, with sizes ranging from 1.3B to 33B versions. Pre-trained on 2 trillion tokens across 80 programming languages, these models boast a 16K window size for project-level code completion and infilling, achieving state-of-the-art performance among open code models.
Blog

Prerequisites
Before you get started with the DeepSeek Coder AMI, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Basic knowledge of AWS services, including EC2 instances and CloudFormation.
- An active AWS account with appropriate permissions.
- Enough vCPU limit to create g5g type instances
(Follow https://meetrix.io/articles/how-to-increase-aws-quota/ blog to ensure this)
Launching the AMI
Step 1: Find and Select 'DeepSeek Coder' AMI
- Log in to your AWS Management Console.
- Follow the provided links to access the 'DeepSeek Coder' product you wish to set up
a. DeepSeek-Coder-6.7B Instruct
b. DeepSeek-Coder-33B Instruct
Step 2: Initial Setup & Configuration
- Click the "Continue to Subscribe" button.
- After subscribing, you will need to accept the terms and conditions. Click on "Accept Terms" to proceed.
- Please wait for a few minutes while the processing takes place. Once it's completed, click on "Continue to Configuration".
- Select the "CloudFormation Template" as the fulfilment option and choose your preferred region on the "Configure this software" page. Afterward, click the "Continue to Launch" button.
- From the "Choose Action" dropdown menu in "Launch this software" page, select "Launch CloudFormation" and click "Launch" button.
Create CloudFormation Stack
Step1: Create stack
- Ensure the "Template is ready" radio button is selected under "Prepare template".
2. Click "Next".
Step2: Specify stack options
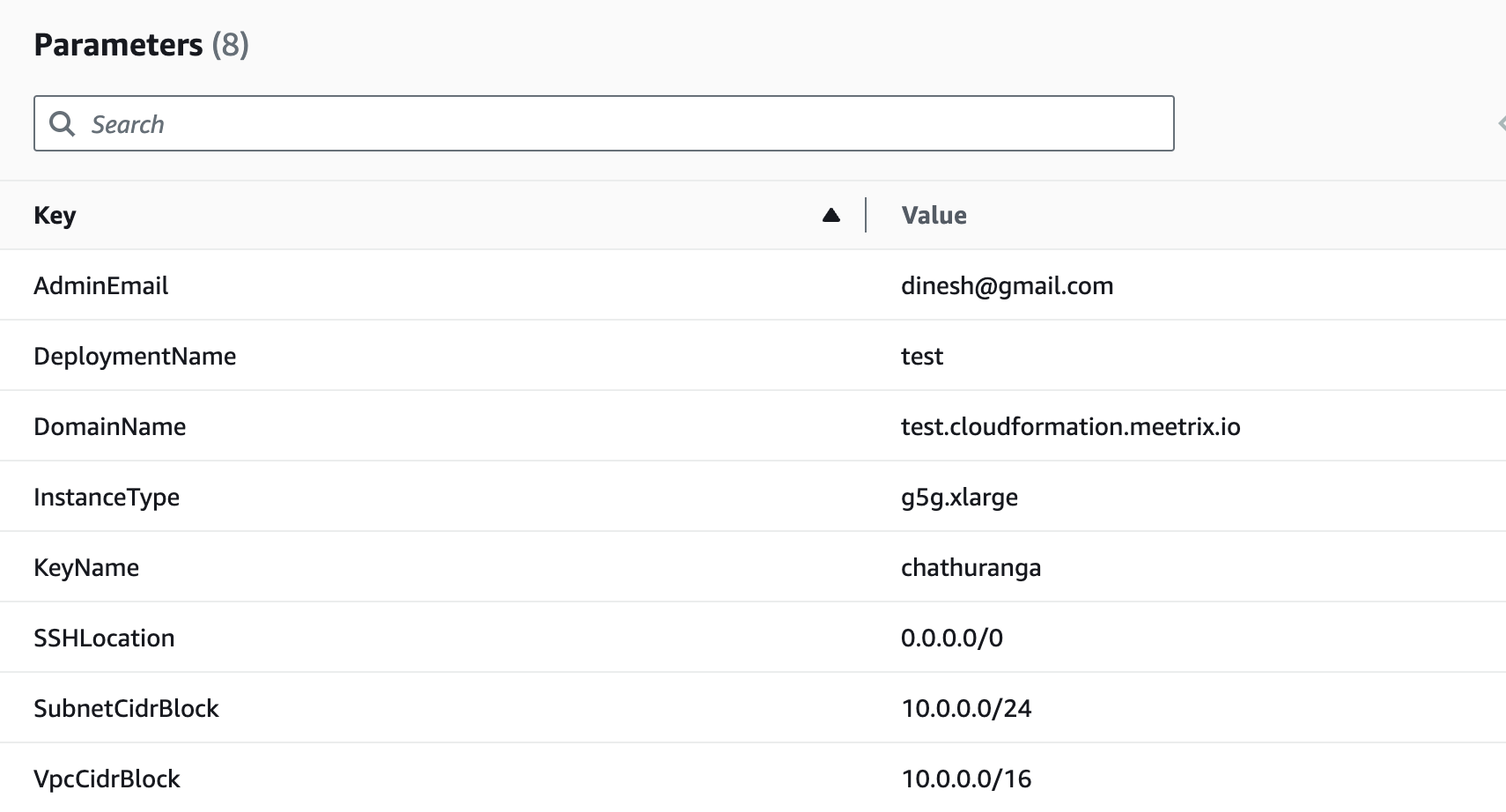
- Provide a unique "Stack name".
- Provide the "Admin Email" for SSL generation.
- For "DeploymentName", enter a name of your choice.
- Provide a public domain name for "DomainName". (Deepseekcoder will automatically try to setup SSL based on provided domain name, if that domain hosted on Route53. Please make sure your domain name hosted on route53. If its unsuccessful then you have to setup SSL manually)
- Choose an instance type, "InstanceType" (We recommend using the default instance type).
- Select your preferred "keyName".
- Set "SSHLocation" as "0.0.0.0/0".
- Keep "SubnetCidrBlock" as "10.0.0.0/24".
- Keep "VpcCidrBlock" as "10.0.0.0/16".
- Click "Next".
Step3: Configure stack options
- Choose "Roll back all stack resources" and "Delete all newly created resources" under the "Stack failure options" section.
- click "Next".
Step4: Review
- Review and verify the details you've entered.
2. Tick the box that says, "I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources with custom names".

3. Click "Submit".
Afterward, you'll be directed to the CloudFormation stacks page.
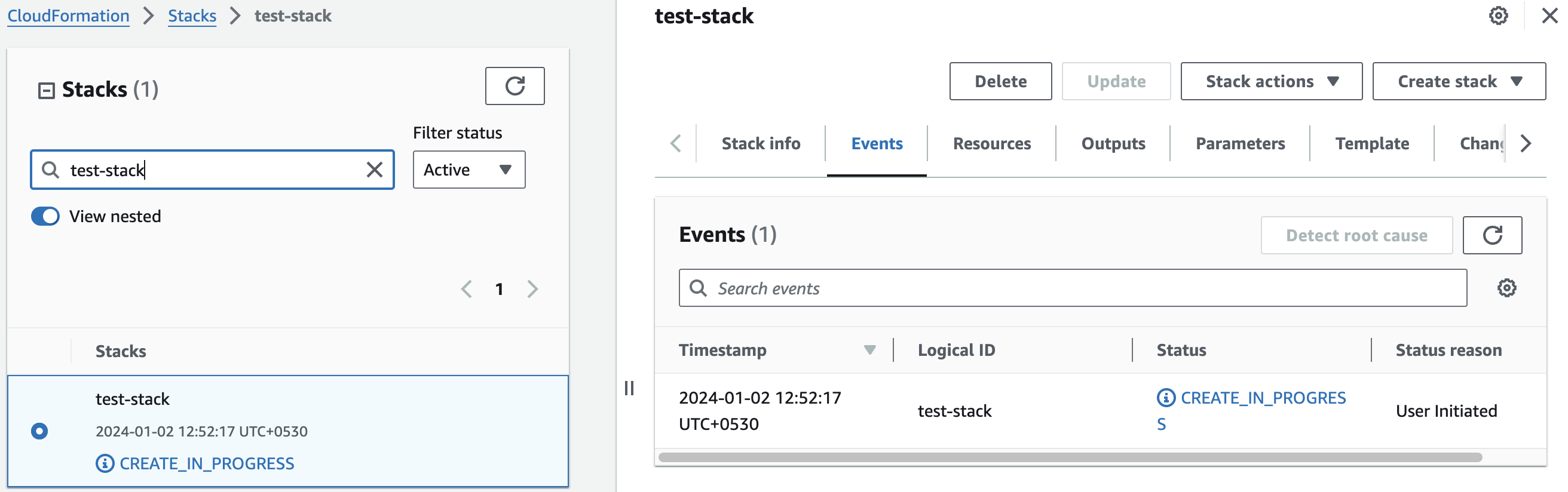
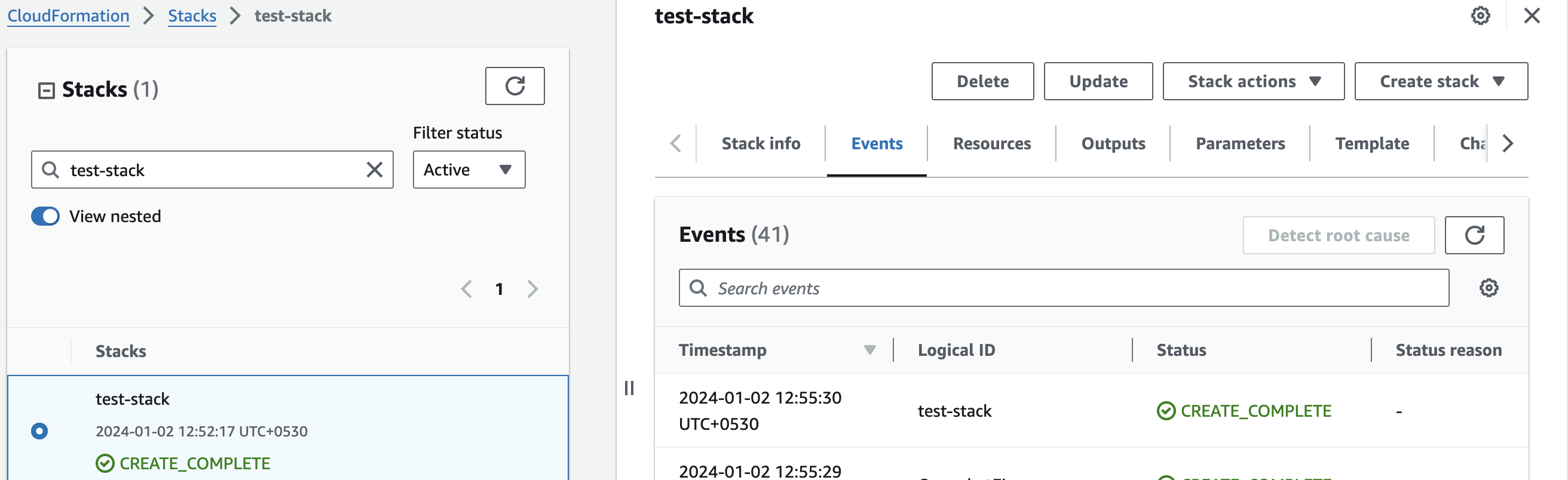
Please wait for 5-10 minutes until the stack has been successfully created.
Update DNS
Step1: Copy IP Address
- Copy the public Ip labeled "PublicIp" in the "Outputs" tab.
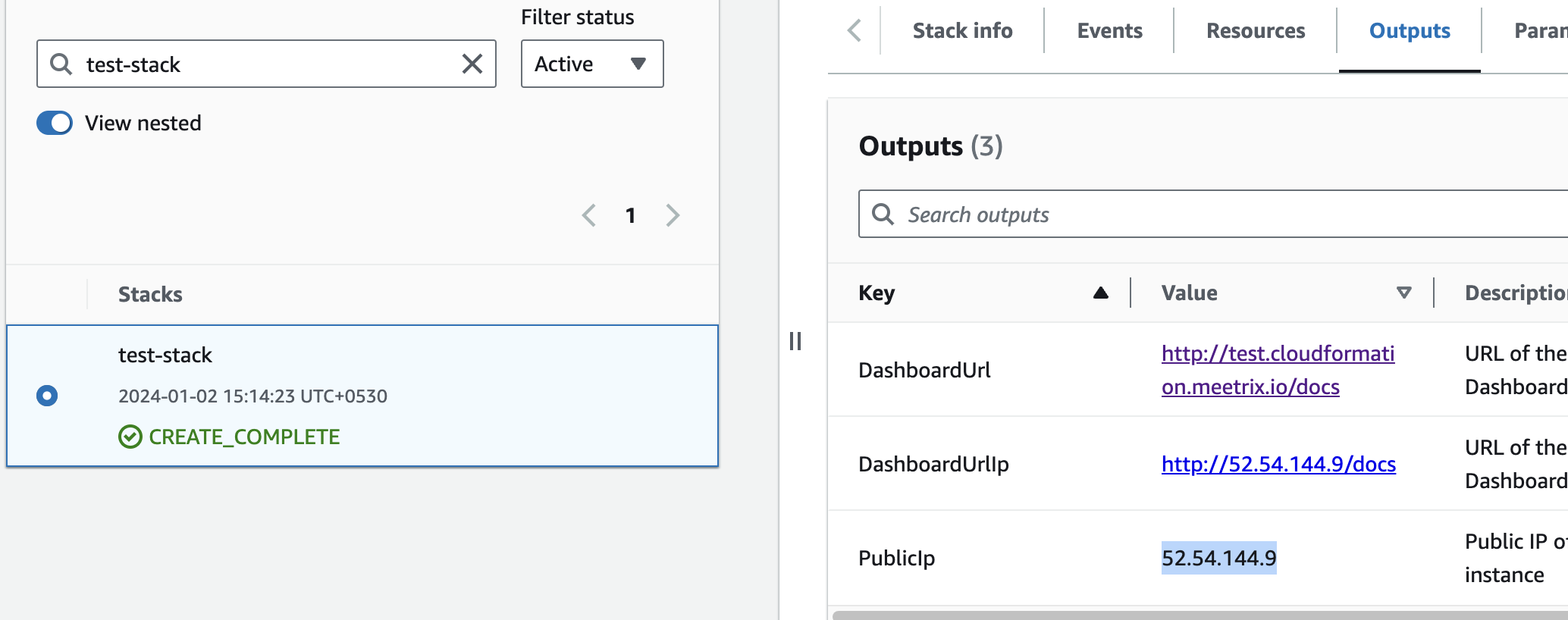
Step2: Update DNS
- Go to AWS Route 53 and navigate to "Hosted Zones".
- From there, select the domain you provided to "DomainName".
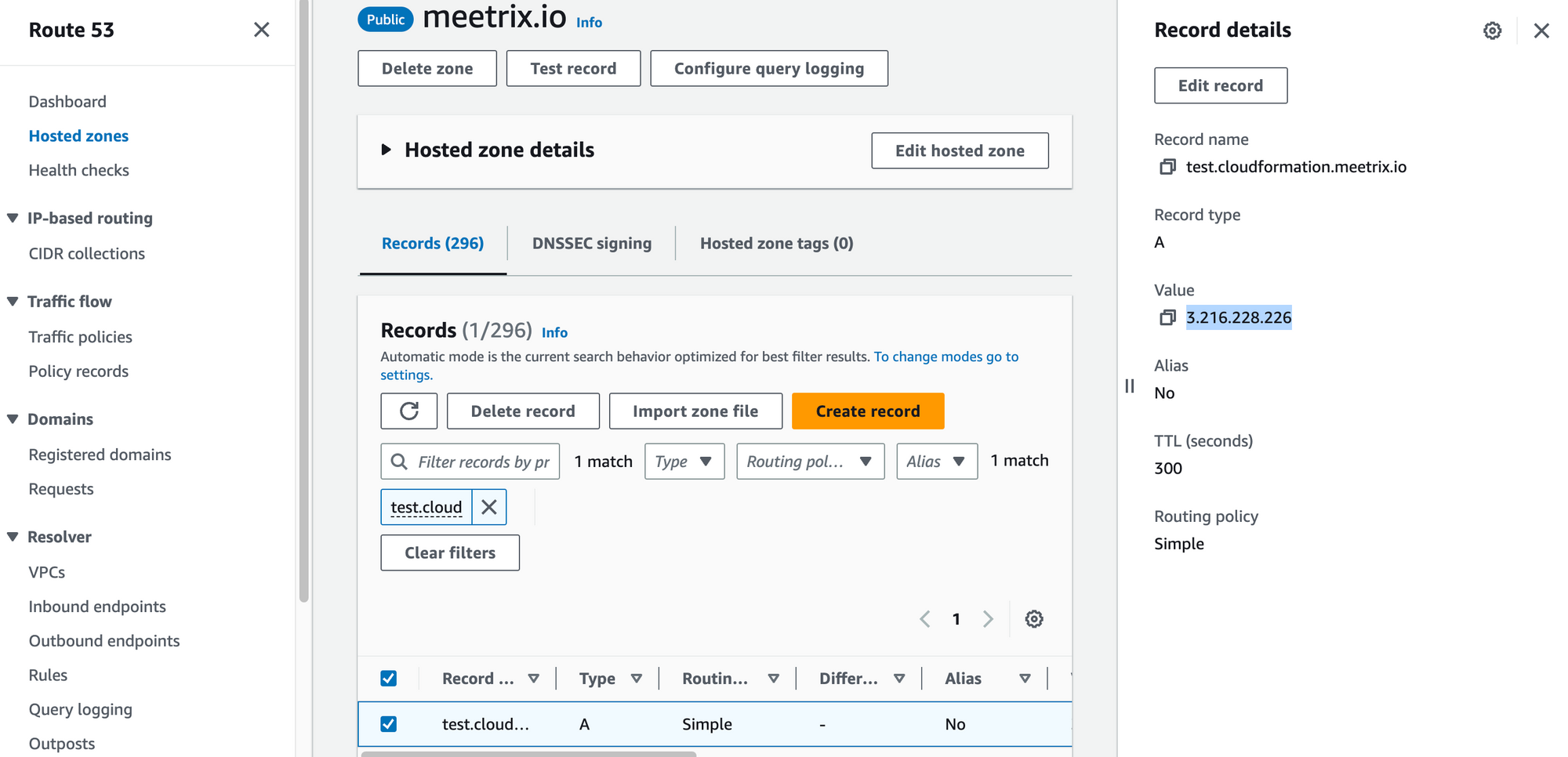
3. Click "Edit record" in the "Record details" and then paste the copied "PublicIp" into the "value" textbox.
4. Click "Save".
Access Deepseek coder
You can access the Deepseek coder application through the "DashboardUrl" or 'DashboardUrlIp' provided in the "Outputs" tab.
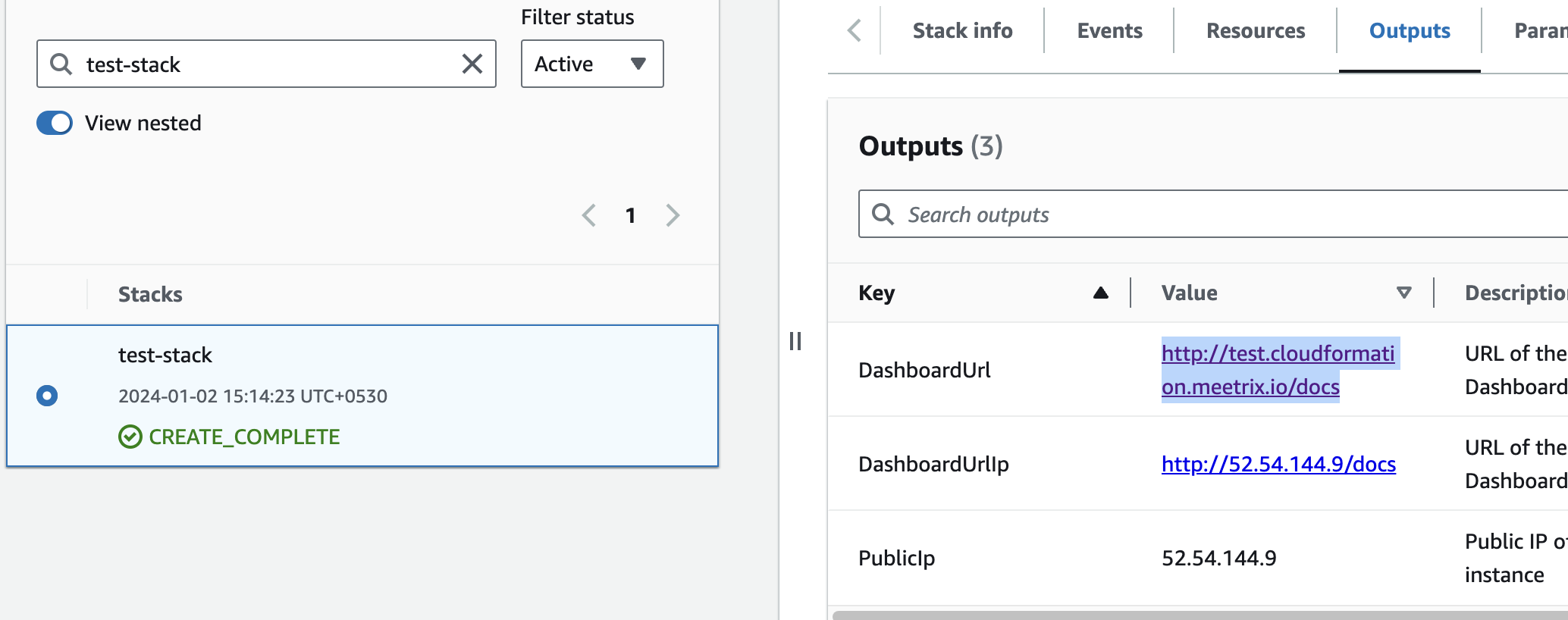
(If you encounter a "502 Bad Gateway error", please wait for about 5 minutes before refreshing the page)
Generate SSL Manually
DeepSeek Coder will automatically try to setup SSL based on provided domain name, if that domain hosted on Route53. If its unsuccessful then you have to setup SSL manually.
Step1: Copy IP Address
- Proceed with the instructions outlined in the above "Update DNS" section, if you have not already done so.
2. Copy the Public IP address indicated as "PublicIp" in the "Outputs" tab.

Step2: Log in to the server
- Open the terminal and go to the directory where your private key is located.
- Paste the following command into your terminal and press Enter:
ssh -i <your key name> ubuntu@<Public IP address>.
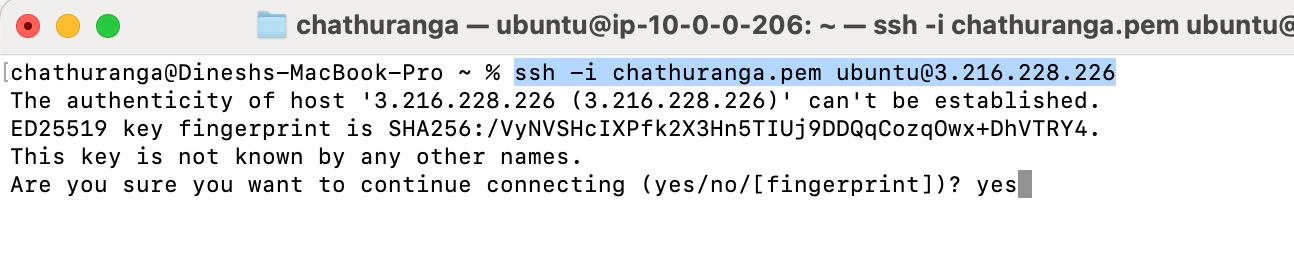
3. Type "yes" and press Enter. This will log you into the server.
Step3: Generate SSL
Paste the following command into your terminal and press Enter and follow the instructions:
sudo /root/certificate_generate_standalone.sh
Admin Email is acquiring for generate SSL certificates.
Shutting Down Deepseek coder
- Click the link labeled "Deepseekcoder" in the "Resources" tab to access the EC2 instance, you will be directed to the Deepseekcoder instance in EC2.
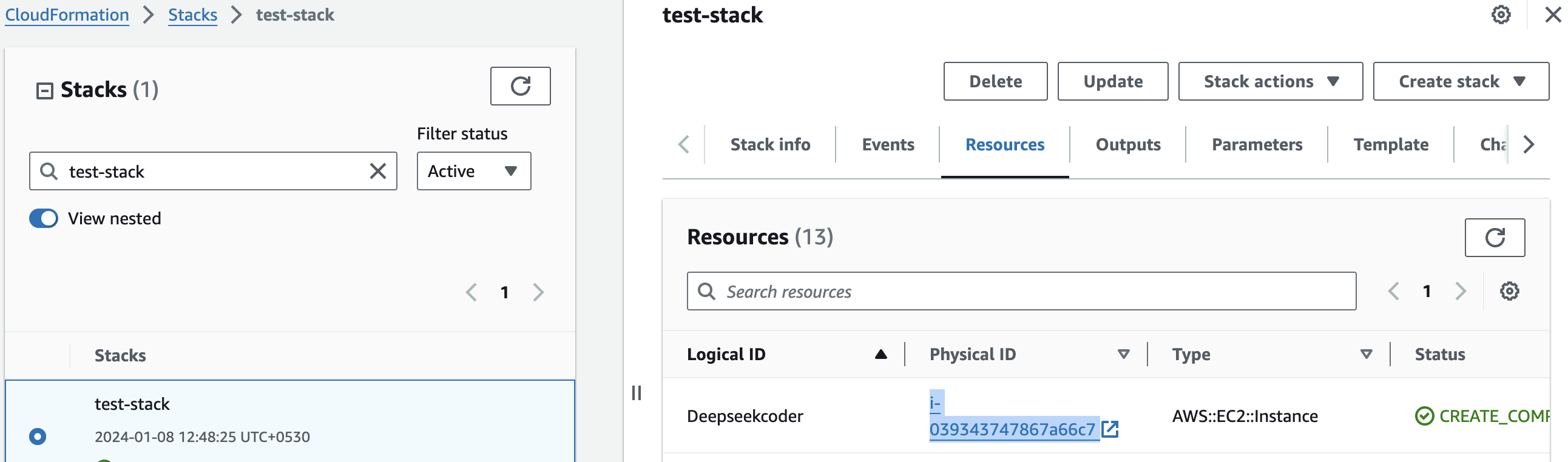
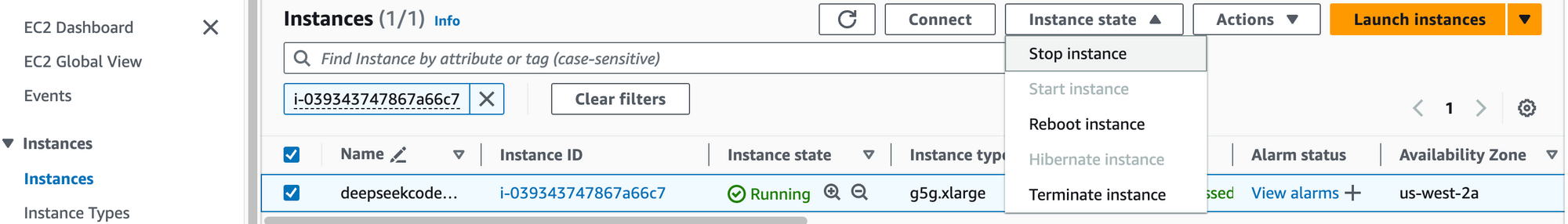
2. Select the instance by marking the checkbox and click "Stop instance" from the "Instance state" dropdown. You can restart the instance at your convenience by selecting "Start instance".
Remove DeepSeek Coder
Delete the stack that has been created in the AWS Management Console under 'CloudFormation Stacks' by clicking the 'Delete' button.
API Documentation
1. Retrieve Completions
Retrieves completions based on the provided prompt.
- Endpoint: /v1/completions
- Method: POST
- Request Body:
{
"prompt": "\n\n### Instructions:\nWhat is the purpose of a variable in programming?\n\n### Response:\n",
"stop": [
"\n",
"###"
]
}- Response Body:
{
"id": "cmpl-309db53c-d281-4fcd-adfb-c1f0175e8a02",
"object": "text_completion",
"created": 1704707291,
"model": "/root/models/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct.Q5_K_M.gguf",
"choices": [
{
"text": "In programming, a variable holds information that can be used and manipulated by the program. A variable's value can change throughout the execution of the code. It has two key characteristics: it has a name (or identifier), which tells other developers what kind of data is stored in the variable, and the actual data itself, which gets stored at runtime. The type of data that a variable holds determines its behavior. Variables are used to store data temporarily for use within an algorithm or program.",
"index": 0,
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 24,
"completion_tokens": 101,
"total_tokens": 125
}
}2. Retrieve Embeddings
Retrieves embeddings based on the provided input text.
- Endpoint: /v1/embeddings
- Method: POST
- Request Body:
{
"input": "The food was delicious and the waiter..."
}- Response Body:
{
"object": "list",
"data": [
{
"object": "embedding",
"embedding": [
-0.07521496713161469,
0.44098934531211853,
0.6786724328994751,
...
],
"index": 0
}
],
"model": "/root/models/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct.Q5_K_M.gguf",
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 10,
"total_tokens": 10
}
}
3. Retrieve Chat Completions
- Endpoint: /v1/chat/completions
As Deepseek Coder is not optimized for chat completion. Please refrain from using this specific endpoint.
4. List Models
Retrieves a list of available models.
- Endpoint: /v1/models
- Method: GET
- Response Body:
{
"object": "list",
"data": [
{
"id": "/root/models/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1.Q4_K_M.gguf",
"object": "model",
"owned_by": "me",
"permissions": []
}
]
}Testing the API
- Create a directory
- Create 3 files (Full codes are given below)
app.js
package.json
.env - Run the following command
npm install - Edit variable file (.env)
- Run the following command
npm start - You will get the responses
const axios = require('axios');
require('dotenv').config();
const makePostRequest = async (url, data, timeout) => {
try {
const response = await axios.post(url, data, { timeout });
return { success: response.status === 200, data: response.data };
} catch (error) {
return { success: false, error: error.message };
}
};
const makeGetRequest = async (url, timeout) => {
try {
const response = await axios.get(url, { timeout });
return { success: response.status === 200, data: response.data };
} catch (error) {
return { success: false, error: error.message };
}
};
const printResponseData = (endpoint, data) => {
console.log(`Response for ${endpoint}:`);
console.log(JSON.stringify(data, null, 2));
console.log('');
};
const checkEndpoints = async () => {
const baseUrl = process.env.BASE_URL;
const model = process.env.MODEL;
const endpoints = [
{ path: '/completions', method: makePostRequest, data: { "model": model, "prompt": process.env.PROMPT1 }, printEnv: 'PRINT_COMPLETIONS_RESPONSE' },
{ path: '/embeddings', method: makePostRequest, data: { "input": process.env.PROMPT2, "model": model }, printEnv: 'PRINT_EMBEDDINGS_RESPONSE' },
{ path: '/chat/completions', method: makePostRequest, data: { "messages": [{ "content": "You are a helpful assistant.", "role": "system" }, { "content": process.env.PROMPT1, "role": "user" }], "model": model }, printEnv: 'PRINT_CHAT_COMPLETIONS_RESPONSE' },
{ path: '/models', method: makeGetRequest, printEnv: 'PRINT_MODELS_RESPONSE' }
];
for (const endpoint of endpoints) {
const url = `${baseUrl}${endpoint.path}`;
const { success, data, error } = await endpoint.method(url, endpoint.method === makePostRequest ? endpoint.data : null, process.env.REQUEST_TIMEOUT || 50000);
const printResponse = process.env[endpoint.printEnv] === 'true';
if (success) {
console.log(`*** Endpoint ${endpoint.path} is reachable.`);
if (printResponse) {
printResponseData(endpoint.path, data);
}
console.log('');
} else {
console.log(`*** Endpoint ${endpoint.path} is not reachable. Error:`, error);
}
}
};
checkEndpoints();
{
"name": "test-llama",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "node app.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"axios": "^1.6.7",
"dotenv": "^16.4.1"
}
}
# Base URL for the API
BASE_URL=https://mixtral-test-prod.meetrix.io/v1
# Model to be used in requests
MODEL=mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1
# Prompts for different endpoints
# /completions and /chat/completions
PROMPT1=What is the capital of France?
# /embeddings
PROMPT2=The food was delicious and the waiter...
# Whether to print responses for each endpoint
PRINT_COMPLETIONS_RESPONSE=true
PRINT_EMBEDDINGS_RESPONSE=false
PRINT_CHAT_COMPLETIONS_RESPONSE=true
PRINT_MODELS_RESPONSE=true
# Timeout for requests in milliseconds (default is 50000)
REQUEST_TIMEOUT=50000
Check Server Logs
Step1: Log in to the server
- Open the terminal and go to the directory where your private key is located.
- Paste the following command into your terminal and press Enter:
ssh -i <your key name> ubuntu@<Public IP address>
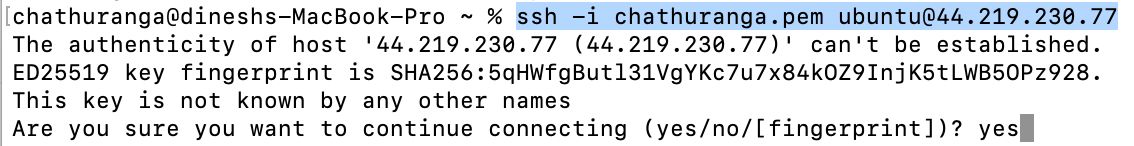
3. Type "yes" and press Enter. This will log you into the server.
Step2: Check the logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
Upgrades
When there is an upgrade, we will update the product with a newer version. You can check the product version in AWS Marketplace. If a newer version is available, you can remove the previous version and launch the product again using the newer version. Remember to backup the necessary server data before removing.
Troubleshoot
- If you face the following error, please follow https://meetrix.io/articles/how-to-increase-aws-quota/ blog to increase vCPU quota.
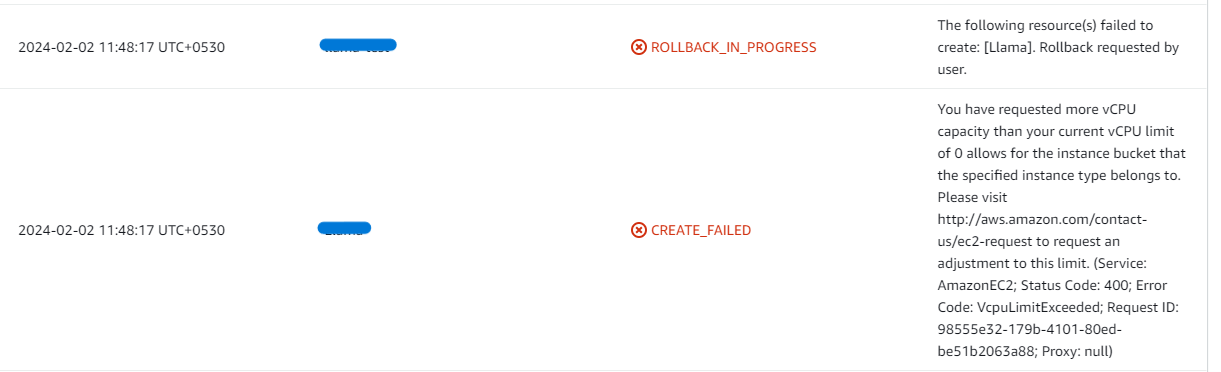
2. If you face the following error (do not have sufficient <instance_type> capacity...) while creating the stack, try changing the region or try creating the stack at a later time.
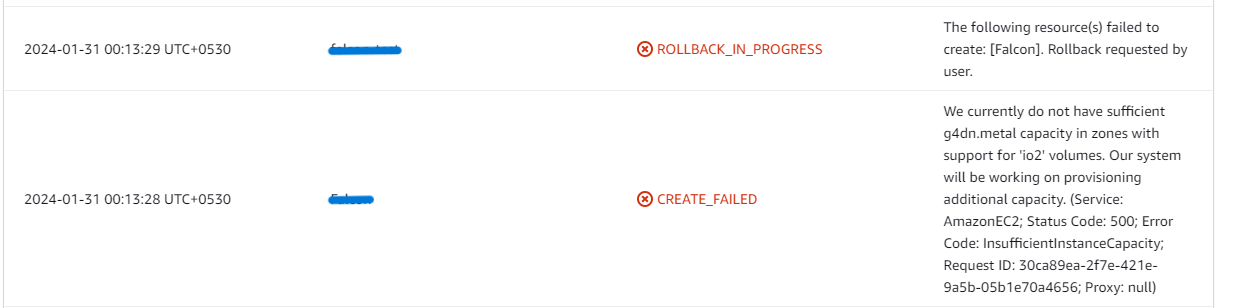
3. If you face the below error, when you try to access the API dashboard, please wait 5-10 minutes and then try.
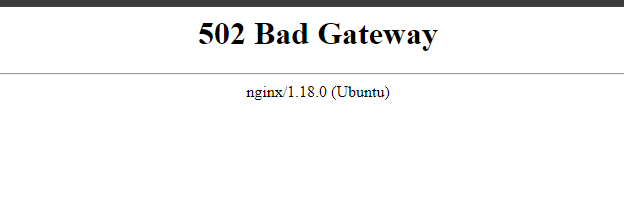
Conclusion
Finally, for a smooth integration of the advanced DeepSeek Coder series into your development environment, the Meetrix DeepSeek Coder Developer Guide is your go-to reference. Our guide provides clear, detailed instructions for all skill levels, regardless of prior coding experience. DeepSeek Coder provides state-of-the-art performance in project-level code completion and infilling with sizes ranging from 1.3B to 33B versions, pre-trained on 2 trillion tokens spanning 80 programming languages. With the Meetrix DeepSeek Coder Developer Guide, you can elevate your coding experience with confidence.
Technical Support
Reach out to Meetrix Support (support@meetrix.io) for assistance with Mixtral issues.